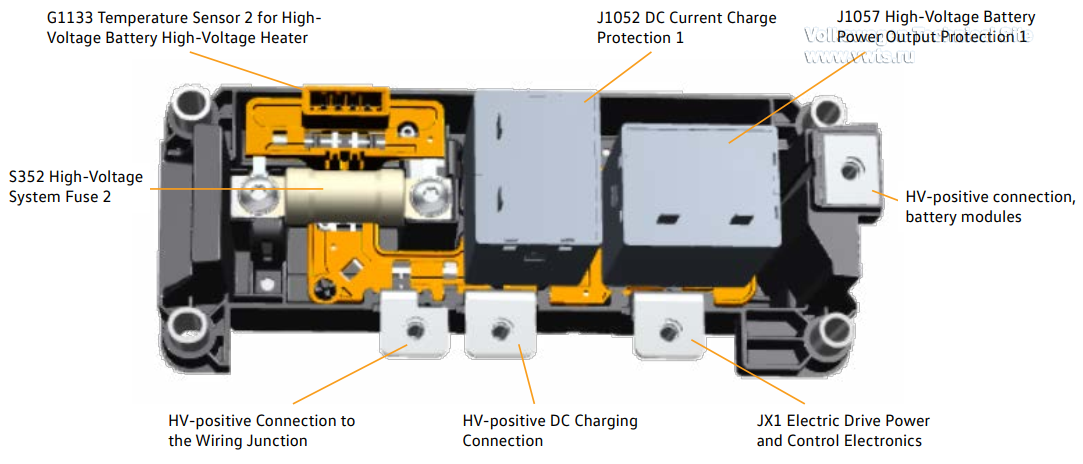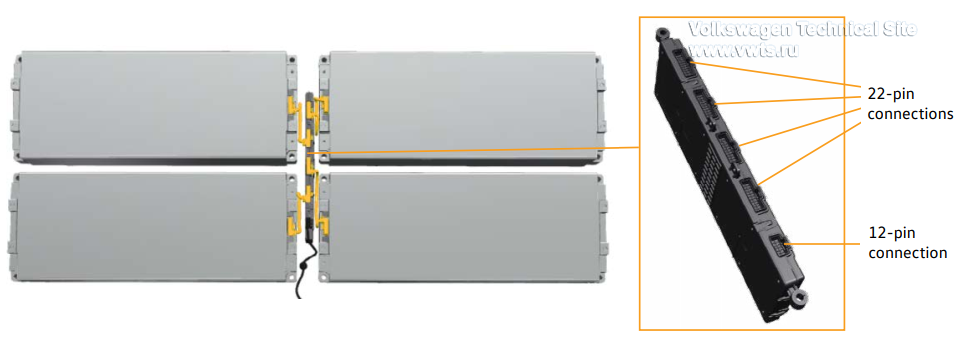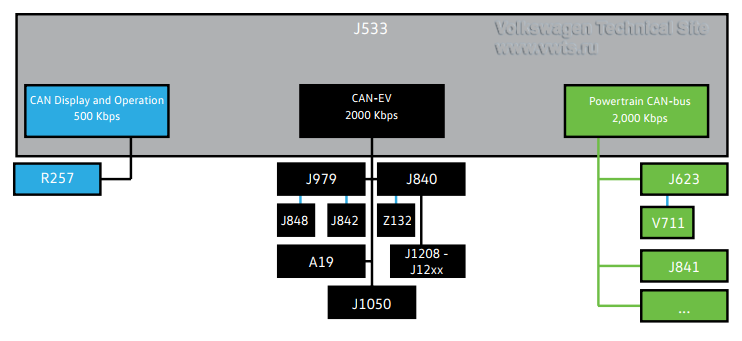
Network
The control units for the high-voltage components are connected to two data-bus
systems.
Both are 2,000 kBaud, ensuring high-speed information exchange.
CAN EV
Powertrain CAN bus
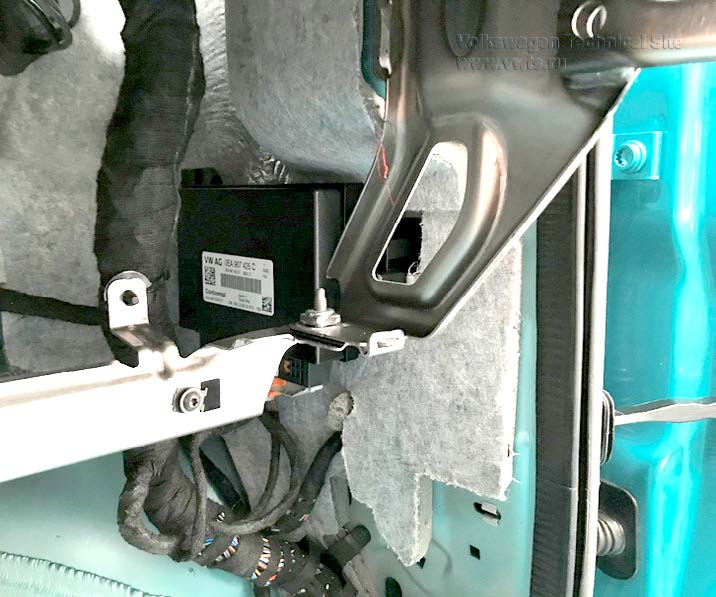
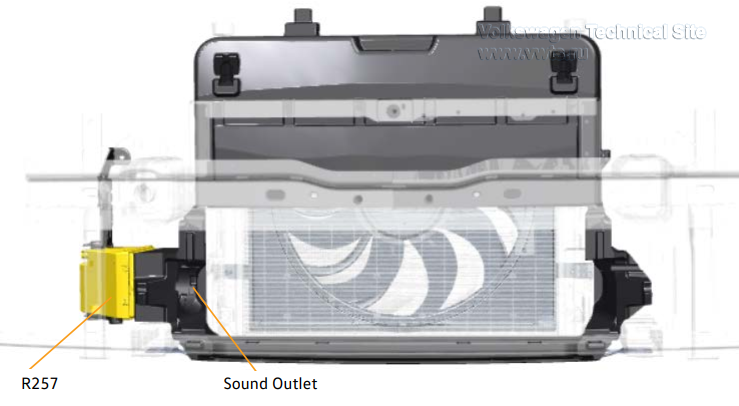
Actuator 1 for Engine Sound Generator R257 is controlled by the CAN Display and
Operation unit.



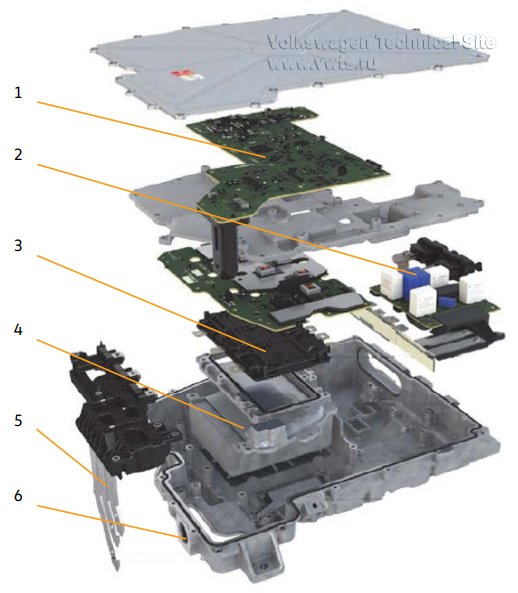

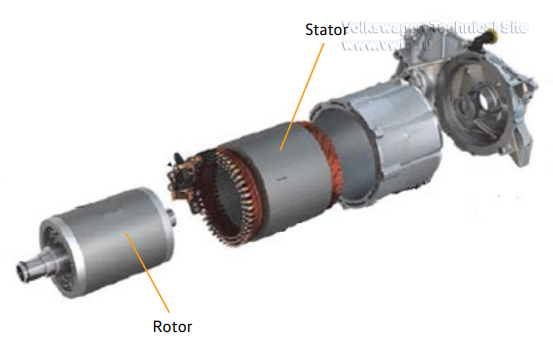
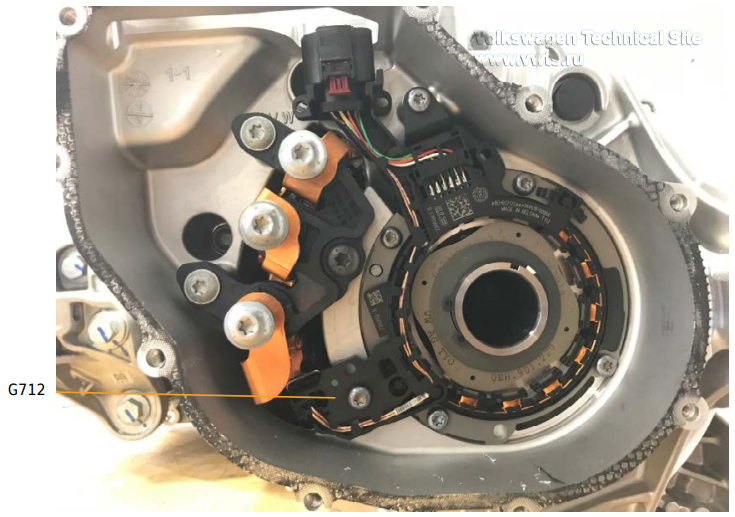

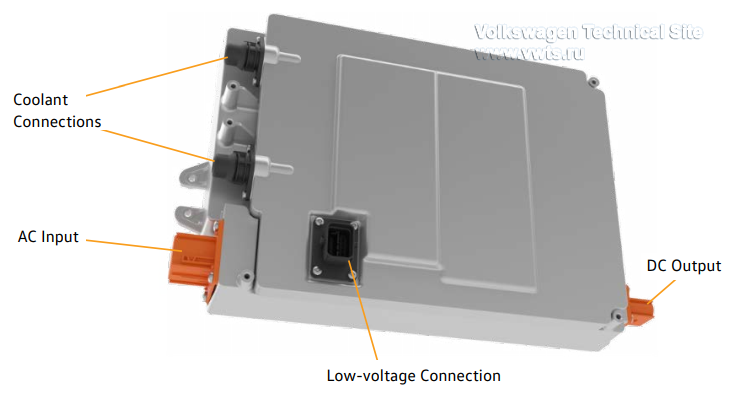
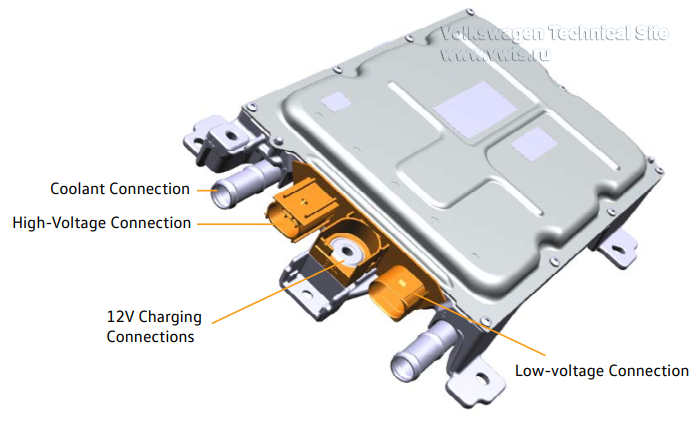
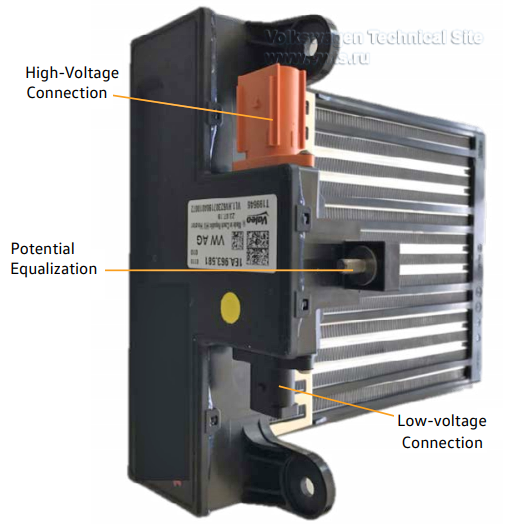
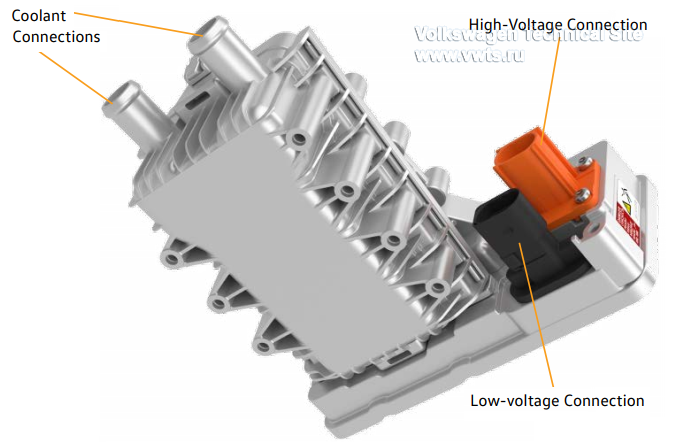
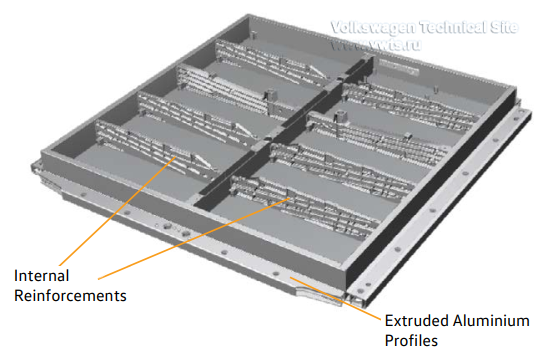
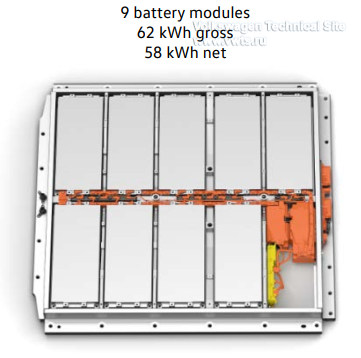
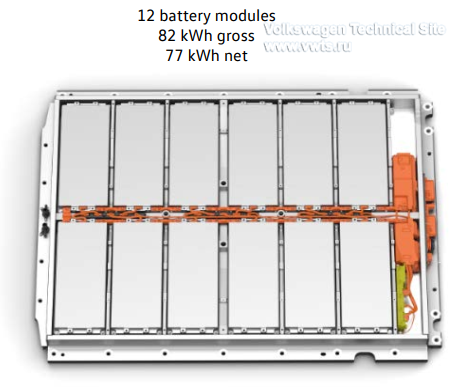

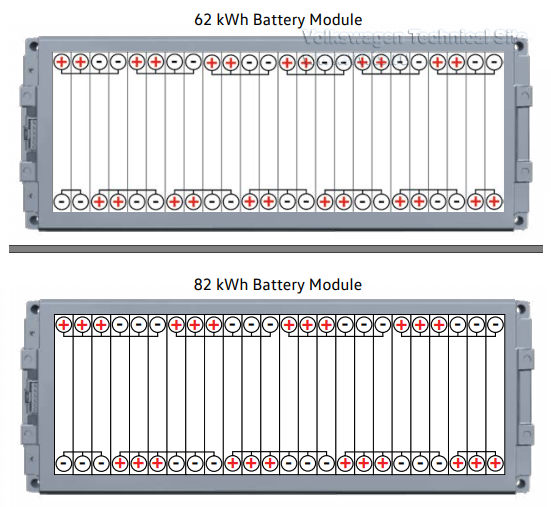
| 62 kWh | 82 kWh | |
| Cell technology | Lithium-ion | Lithium-ion |
| Cell type | Prismatic | Prismatic |
| Manufacturer | LG | LG |
| Capacity per battery cell | 78 Ah | 78 Ah |
| Number of cells | 24 | 24 |
| Circuitry of the module | 12 in series, 2 in parallel | 8 in series, 3 in parallel |
| Number of modules in battery | 9 | 12 |
| Capacity of the module | 156 Ah | 234 Ah |
| Nominal voltage of the module | 44.4 V | 29.6 V |
| Energy content of the module | 6.926 kWh | 6.926 kWh |
| Weight per module | approx. 66 lbs (30 kg) | approx. 66 lbs (30 kg) |