The VW ID.4 Wiring and Connector Concept
Key
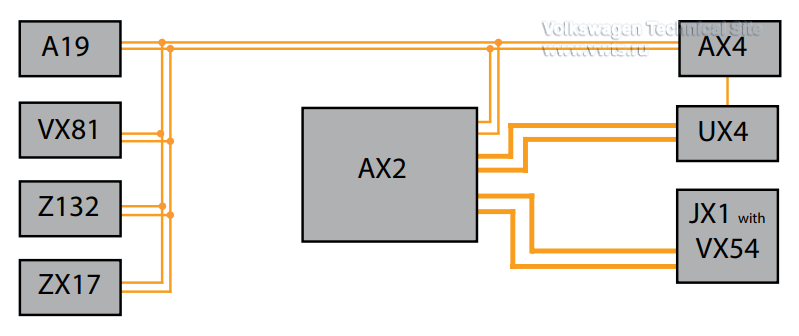
A19 Voltage Converter
AX2 High-Voltage Battery 1
AX4 High-Voltage Battery Charger 1
JX1 Electric Drive Power and Control Electronics
UX4 High-Voltage Battery Charging Socket 1
VX54 Three-Phase Current Drive
VX81 A/C Compressor
Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3
ZX17 High-Voltage Heater (PTC)
Wiring Junctions
The components do not require power distribution panels. They are replaced by wiring junctions in the high-voltage wiring harnesses.
The wiring junctions in the rear area connect AX4 High-Voltage Battery Charger 1 to AX2 High-Voltage Battery 1 and the high-voltage components in the front of the vehicle.
The wiring junction in the front of the vehicle connects the Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3, the VX81 A/C Compressor, the A19 Voltage Converter and the ZX17
High-Voltage Heater (PTC) to the components in the rear of the vehicle.
The small connectors in the high-voltage circuit are glued during production and cannot be separated.
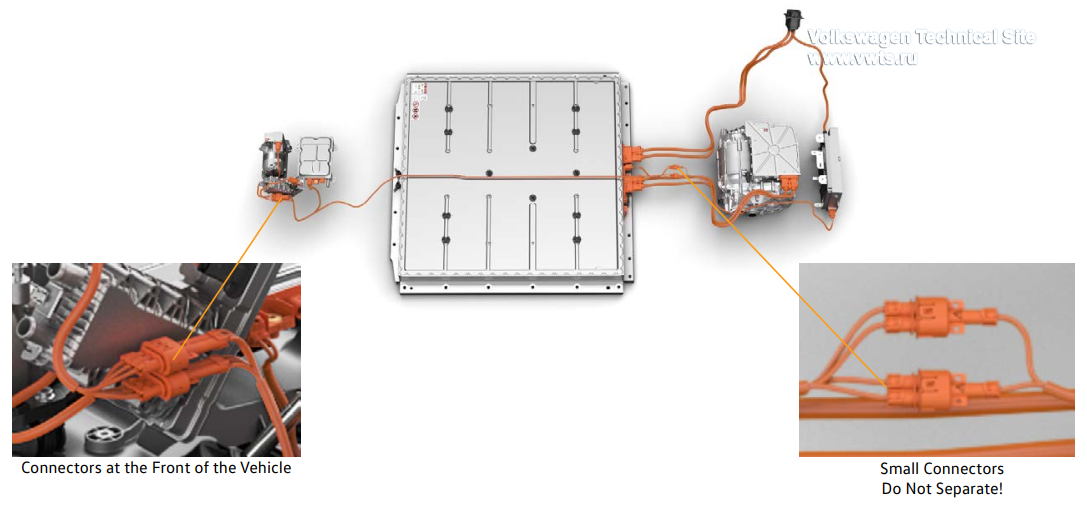
Connector Concept
The connectors of high-voltage components are required to protect against foreign objects touching the contacts that carry life-threatening voltage.
This is known as Ingress Protection (IP).
The connectors on MEB vehicles have been designed with a higher ingress protection standard to ensure a greater degree of protection against penetration of a solid object (such as a finger).
Because of this new connector concept with heightened touch protection, there is no longer need for a “pilot line” between all components in the high-voltage system.

The electrical connectors are a new component
developed for advanced accidental contact protection.

All HV wires in the Volkswagen ID.4 are connected mechanically.
No screw connections on the wires are used.

To ensure that the contacts still have the necessary
cross-sections, the connectors are wide.
Table of Contents
High-voltage System Overview
Wiring and Connector Concept
High-voltage System Components
Thermal Management
High-voltage Safety Concept
Driving Mode Selection
Wiring Concept
A new high-voltage wiring concept is being use in Modular Electric
Drive Matrix (MEB) vehicles.
Thanks to the revised electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), shielded
cables are not necessary.
The EMC filters are adapted to the individual requirements of the
different high-voltage components.
They can be made of capacitors, restrictors or more complex
circuitry.

Key
A19 Voltage Converter
AX2 High-Voltage Battery 1
AX4 High-Voltage Battery Charger 1
JX1 Electric Drive Power and Control Electronics
UX4 High-Voltage Battery Charging Socket 1
VX54 Three-Phase Current Drive
VX81 A/C Compressor
Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3
ZX17 High-Voltage Heater (PTC)
Wiring Junctions
The components do not require power distribution panels. They are replaced by wiring junctions in the high-voltage wiring harnesses.
The wiring junctions in the rear area connect AX4 High-Voltage Battery Charger 1 to AX2 High-Voltage Battery 1 and the high-voltage components in the front of the vehicle.
The wiring junction in the front of the vehicle connects the Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3, the VX81 A/C Compressor, the A19 Voltage Converter and the ZX17
High-Voltage Heater (PTC) to the components in the rear of the vehicle.
The small connectors in the high-voltage circuit are glued during production and cannot be separated.

Connector Concept
The connectors of high-voltage components are required to protect against foreign objects touching the contacts that carry life-threatening voltage.
This is known as Ingress Protection (IP).
The connectors on MEB vehicles have been designed with a higher ingress protection standard to ensure a greater degree of protection against penetration of a solid object (such as a finger).
Because of this new connector concept with heightened touch protection, there is no longer need for a “pilot line” between all components in the high-voltage system.

The electrical connectors are a new component
developed for advanced accidental contact protection.

All HV wires in the Volkswagen ID.4 are connected mechanically.
No screw connections on the wires are used.

To ensure that the contacts still have the necessary
cross-sections, the connectors are wide.