Thermal Management
Table of Contents
High-voltage System Overview
Wiring and Connector Concept
High-voltage System Components
Thermal Management
High-voltage Safety Concept
Driving Mode Selection
Battery
All high-voltage batteries in the VW
ID.4 have
an active thermal management system. The aluminium heat sink is located outside
of the battery housing.
This prevents contact between coolant and the high-voltage components inside of
the battery housing.
The high-voltage battery modules are connected to the base of the battery
housing by a thermally conductive paste.
The aluminium heat sink is also connected to the housing base with a thermally
conductive paste.
The solid aluminum underbody guard protects the heat sink from mechanical
damage.
Battery
The coolant temperature sensors are connected directly to the J840 Battery
Regulation Control Module.
The control unit uses the sensor information to regulate the V590 High-Voltage
Battery Coolant Pump.
The battery cooling not only occurs when the vehicle is moving, but can also be
activated during charging. This significantly reduces battery temperature
increases, especially when using DC charging. This allows for a faster charging
rate, even for repeated charging processes.
The high-voltage battery can be both actively cooled and heated. This happens
depending on the internal battery temperature.
• < 46°F: heating by the Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3
• > 95°F (in vehicle operation): cooling by the heat exchanger for heat
condenser
• > 86°C (during charging): cooling by the heat exchanger for heat condenser
It can also be integrated into the low-temperature cooling circuit.
Different operating states are shown on the following pages.
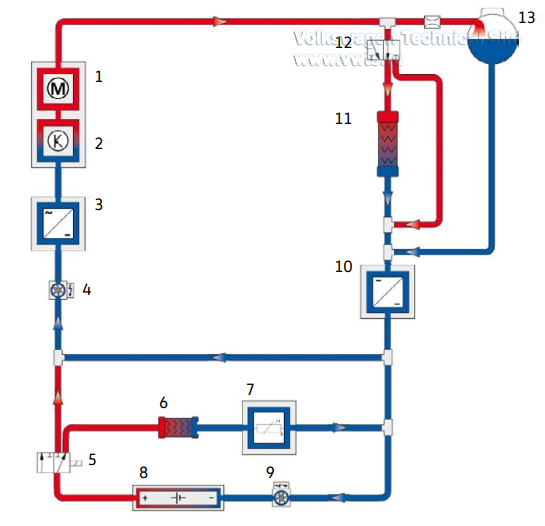
The Coolant Circuit without a Heat Pump
At a temperature of 59°F (15°C) or higher the thermostat opens, allowing coolant
to flow to the radiator.
The mixing valve can be used to integrate the battery into the low-temperature
circuit, or to maintain the correct temperature in a separate circuit with the
Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3.
The J840 Battery Regulation Control Module controls thermal management of the
high-voltage battery.
In the version without a heat pump, it regulates the V683 Mixing Valve for
High-Voltage Battery Warming and the V590 High-Voltage Battery Coolant Pump.
The V468 Low Temperature Circuit Coolant Pump is always activated by the J623
Engine Control Module.
1. VX54 Three-Phase Current Drive
2. JX1 Electric Drive Power and Control Electronics
3. AX4 High-Voltage Battery Charger 1
4. V468 Low Temperature Circuit Coolant Pump
5. V683 Mixing Valve for High-Voltage Battery Warming
6. Heat Exchanger for Heat Condenser
7. Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3
8. AX2 High-Voltage Battery 1
9. V590 High-Voltage Battery Coolant Pump
10. A19 Voltage Converter
11. Radiator
12. Thermostat
13. Coolant Expansion Tank
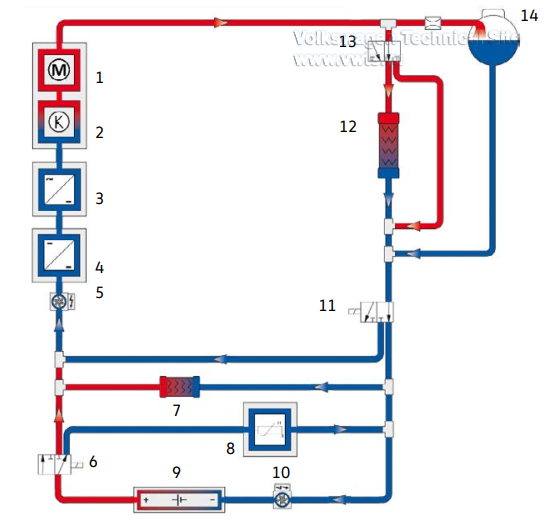
The Coolant Circuit with a Heat Pump (not for US vehicles)
The coolant circuit has been adapted for the ID.4 with a heat pump, including
the V696 Mixing Valve 2 for High-Voltage Battery Warming.
The heat exchanger for heat condenser and the Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3 are
now installed in branches of the coolant circuit that can be separately
controlled.
This is necessary to allow the heat exchanger for heat condenser to be activated
individually when the heat pumps are operating, and to heat the battery using
the Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3 at the same time.
The J840 Battery Regulation Control Module controls thermal management of the
high-voltage battery.
In the version with a heat pump, it regulates the V683 Mixing Valve for
High-Voltage Battery Warming, V696 Mixing Valve 2 for High-Voltage Battery
Warming and the V590 High-Voltage Battery Coolant Pump.
The V468 Low Temperature Circuit Coolant Pump is always activated by the J623. A
number of potential switch variants are shown on the following pages.
1. VX54 Three-Phase Current Drive
2. JX1 Electric Drive Power and Control Electronics
3. AX4 High-Voltage Battery Charger 1
4. A19 Voltage Converter
5. V468 Low Temperature Circuit Coolant Pump
6. V683 Mixing Valve for High-Voltage Battery Warming
7. Heat Exchanger for Heat Condenser
8. Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3
9. AX2 High-Voltage Battery 1
10. V590 High-Voltage Battery Coolant Pump
11. V696 Mixing Valve 2 for High-Voltage Battery Warming
12. Radiator
13. Thermostat
14. Coolant Expansion Tank
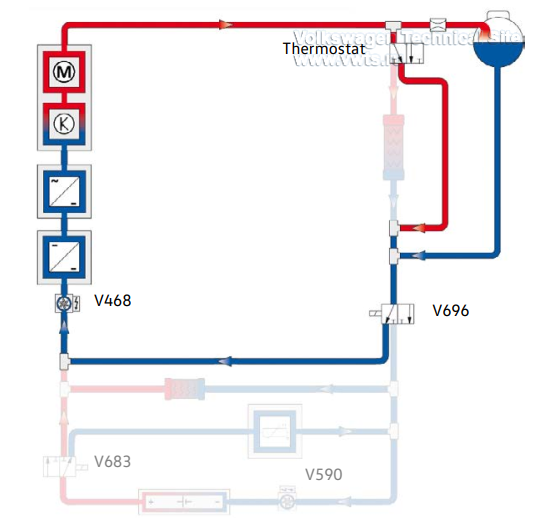
Cooling and Heating Strategies for Vehicles with a Heat Pump (not for US
Vehicles)
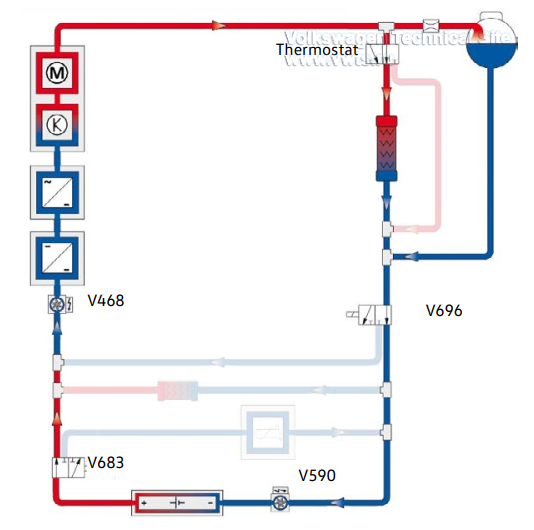
Radiator bypass active - Battery is not cooled or heated
Prerequisites:
• Temperature at the thermostat < 59°F (15°C)
• Battery temperature 47°F (8°C) to 95°F (35°C)
• No demand by the heat pump
The thermostat opens the radiator bypass. The V696 Mixing Valve 2 for
HighVoltage Battery Warming activates the minimum possible low-temperature
cooling circuit.
The V468 Low Temperature Circuit Coolant Pump is activated when the heat pumps
are operating, and to heat the battery using the Z132 Heating Element (PTC) 3 at
the same time.
The versions shown here do not show all possible operating modes.
Other ambient conditions, customer requirements and component temperatures may
require other operating modes.
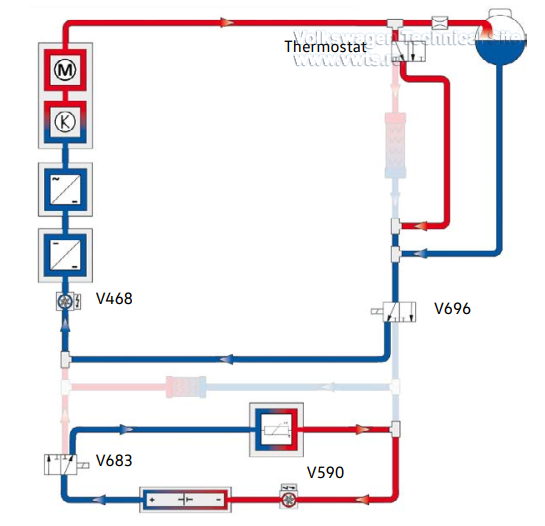
Cooling and Heating Strategies for Vehicles with a Heat Pump (not for US
Vehicles)
Radiator bypass active - Battery is heated
Prerequisites:
• Temperature at the thermostat < 59°F (15°C)
• Battery temperature < 47°F (8°C)
• No demand by the heat pump
The thermostat opens the radiator bypass, then the V696 Mixing Valve 2 for
High-Voltage Battery Warming activates the minimum possible lowtemperature
cooling circuit.
The V683 Mixing Valve for High-Voltage Battery Warming activates the battery
heating circuit. Both coolant pumps are activated.
The versions shown here do not show all possible operating modes.
Other ambient conditions, customer requirements and component temperatures may
require other operating modes.
Cooling and Heating Strategies for Vehicles with a Heat Pump (not for US
Vehicles)
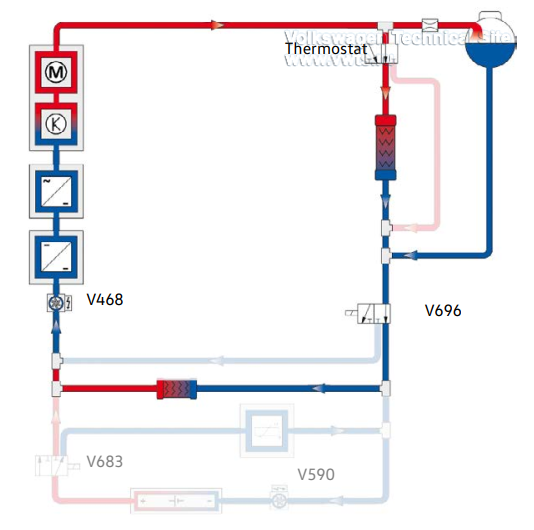
Radiator flow - Battery is not cooled or heated
Prerequisites
• Temperature at the thermostat < 59°F (15°C)
• Battery temperature 47°F (8°C) to 95°F (35°C)
• No demand by the heat pump
The thermostat closes the radiator bypass, then the V696 Mixing Valve 2 for
High-Voltage Battery Warming activates the minimum possible lowtemperature
cooling circuit.
Only the coolant pump for V468 Low Temperature Circuit Coolant Pump is
activated.
Cooling and Heating Strategies for Vehicles with a Heat Pump (not for US
Vehicles)
Radiator flow - The battery is cooled by the heat exchanger for heat condenser
Prerequisites:
• Temperature at the thermostat < 59°F (15°C)
• Battery temperature > 95°F (35°C) in vehicle operation
• Battery temperature > 86°F (30°C) when charging
• No demand by the heat pump
The thermostat closes the radiator bypass, then the V696 Mixing Valve 2 for
High-Voltage Battery Warming activates the minimum possible lowtemperature
cooling circuit.
The V683 Mixing Valve for High-Voltage Battery Warming activates the battery
coolant circuit. Both coolant pumps are activated.
The versions shown here do not show all possible operating modes.
Other ambient conditions, customer requirements and component temperatures may
require other operating modes.
Cooling and Heating Strategies for Vehicles with a Heat Pump (not for US
Vehicles)
Radiator flow - Battery is cooled by low-temperature circuit
Prerequisites:
• Temperature at the thermostat > 59°F (15°C)
• Battery temperature > 86°F (30°C)
• No demand by the heat pump
The thermostat closes the radiator bypass, then the V696 Mixing Valve 2 for
High-Voltage Battery Warming opens the connection to the battery.
The V683 Mixing Valve for High-Voltage Battery Warming activates the battery
coolant circuit. Both coolant pumps are activated.
The versions shown here do not show all possible operating modes.
Other ambient conditions, customer requirements and component temperatures may
require other operating modes.
Cooling and Heating Strategies for Vehicles with a Heat Pump (not for US
Vehicles)
Radiator flow - Battery is not cooled or heated
Prerequisites:
• Temperature at the thermostat > 59°F (15°C)
• Battery temperature 47°F (8°C) to 86°F (30°C)
• Demand by the heat pump
The thermostat closes the radiator bypass, then the V696 Mixing Valve 2 for
High-Voltage Battery Warming opens the connection to the battery.
The V683 Mixing Valve for High-Voltage Battery Warming activates the battery
heating circuit. Only the V468 Low Temperature Circuit Coolant Pump is activated.
The versions shown here do not show all possible operating modes.
Other ambient conditions, customer requirements and component temperatures may
require other operating modes.